Shear Wave and Vs30 Surveys
Southern Geophysical can provide all types of shear wave surveying gained from over 20 years of experience
Shear wave (Vs) and Compressional waves (P-wave or Vp) are important parameters in geotechnical engineering for a range of purposes. Shear wave velocity (Vs) is one of the elastic constants and closely related to Young’s and shear moduli therefore Vs is often used as a direct indicator of the ground strength (stiffness). Vs is also routinely used in the modelling of the ground response during earthquakes. While there are numerous invasive and non-invasive techniques for obtaining a shear wave model of the subsurface, below is a selection of geophysical techniques commonly used. Southern Geophysical can provide all types of shear wave surveying and can assist in selecting the most appropriate.
Crosshole Shear Wave Testing (2-3 Boreholes or SCPT’s)

Downhole Shear Wave Testing (1 Borehole or SCPT)
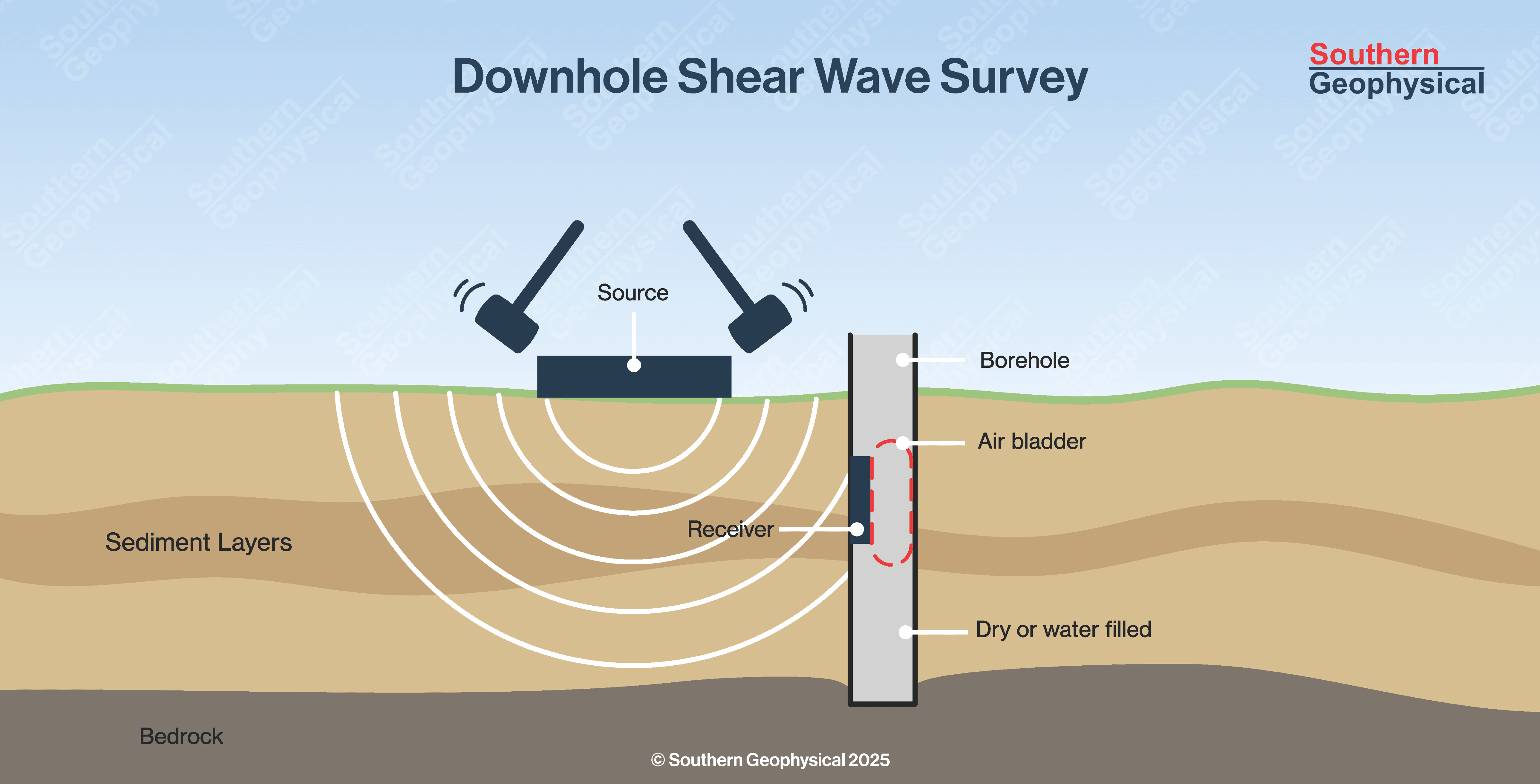
Downhole Testing
Downhole testing, while having a more complex possible wave path than cross hole, is directly measuring the one-way shear wave velocity. This test tends to give a robust velocity model, but due to the vertical wave path may have limitations and errors which need to be included in any Vs values supplied.
Shear Wave Reflection
This method uses the reflection of shear waves from the subsurface horizons to generate a shear wave interval velocity model. Processing is similar to normal shallow P-wave reflection surveys and has similar limitations.
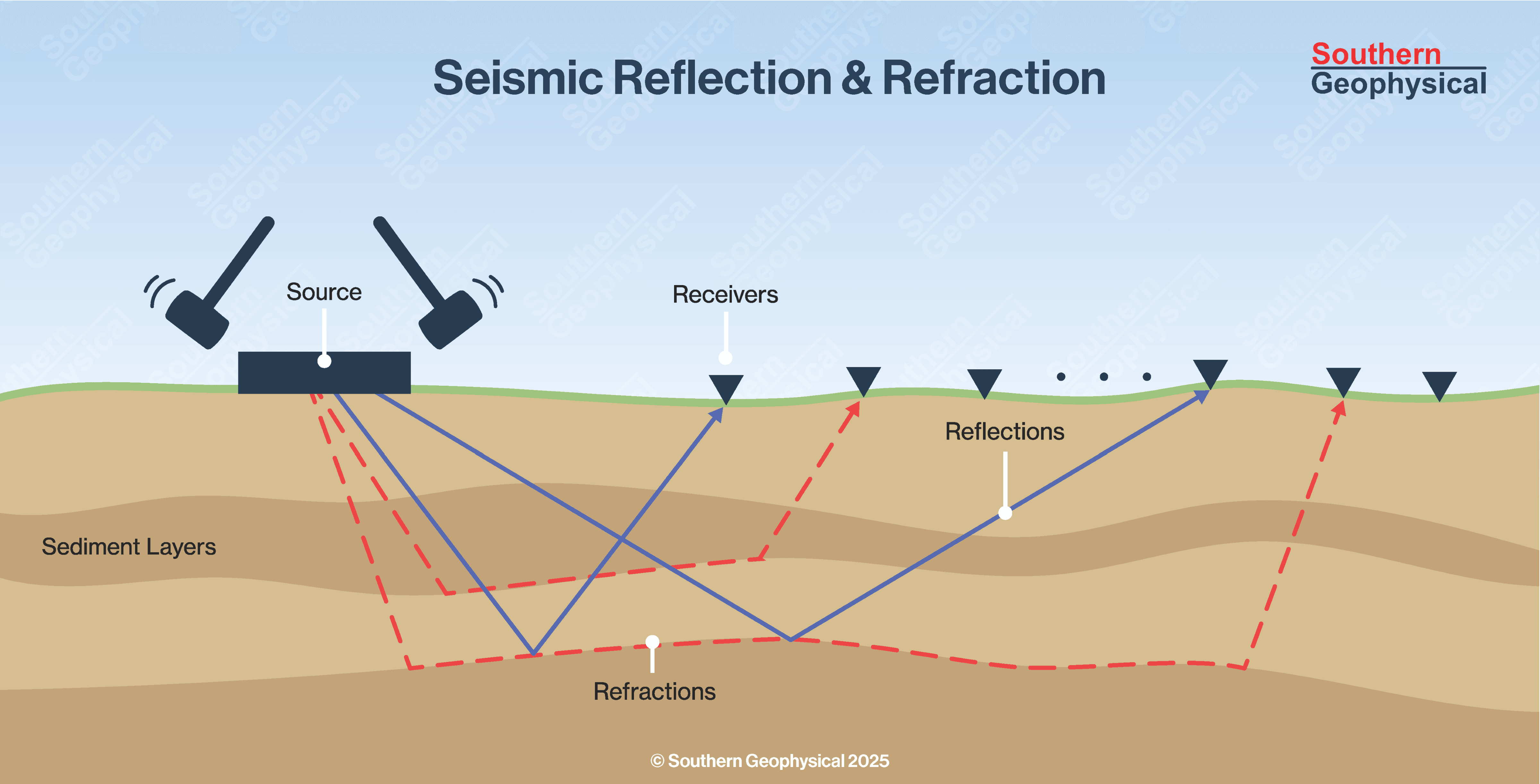
Shear Wave Refraction
The refraction of shear waves from the subsurface horizons are used to generate a shear wave interval velocity model. Processing is similar to normal shallow P-wave refraction tomograph surveys and has similar limitations.
Surface Wave Methods MASW, ReMi, HVSR
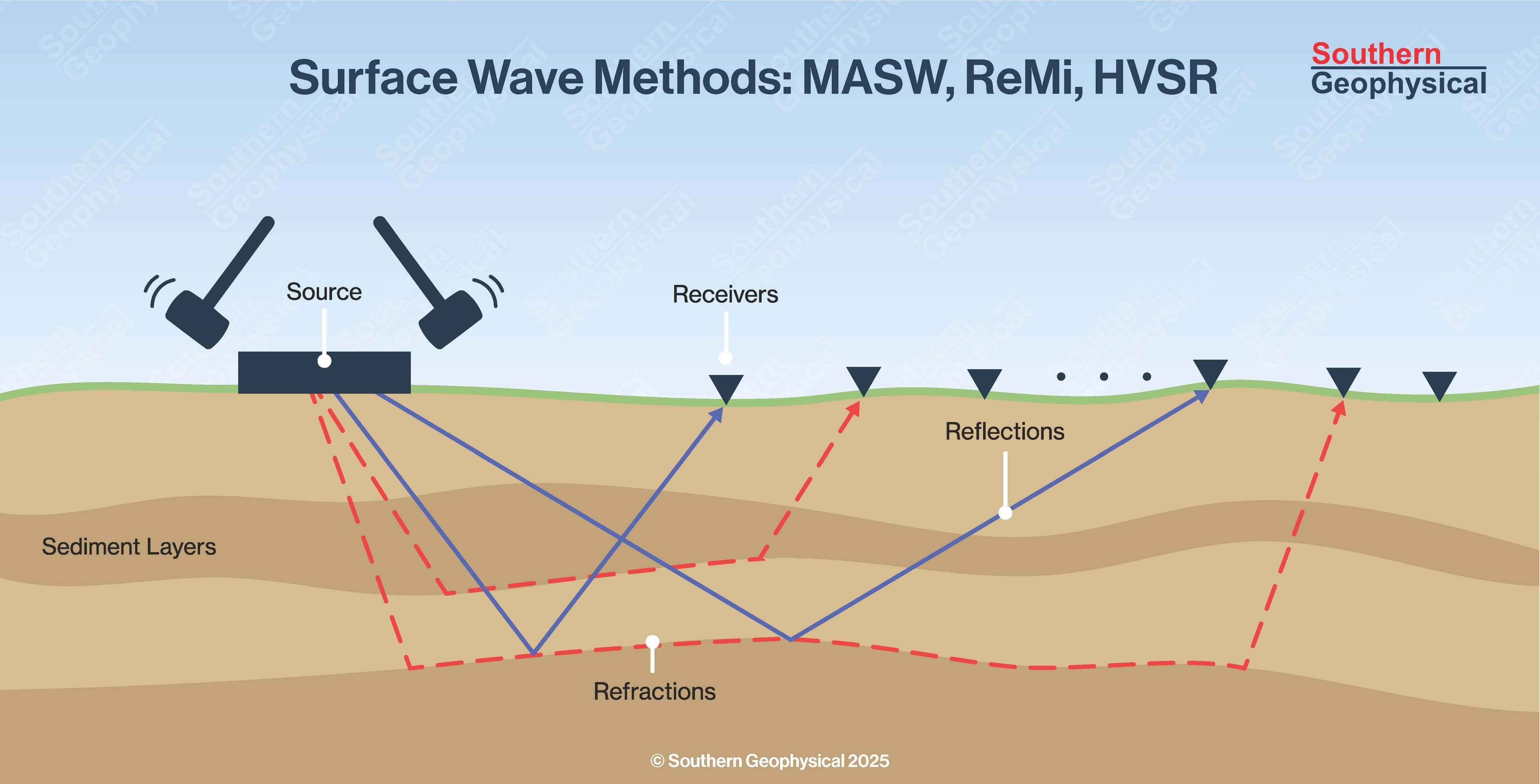
Surface Wave Testing
A shear wave velocity model for the subsurface can be back calculated by determining how surface waves travel along the surface. The unique and sometimes complex velocity and frequency changes of the surface waves as they travel is fundamentally the result of the shear wave velocity distribution of the material below where they are travelling. This dispersive nature of the surface waves is captured by an array of sensors on the surface and used to calculate a possible shear wave model of the subsurface. Since the surface wave dispersion is non-unique (more than one subsurface shear wave velocity structure can give the same surface wave dispersion. Caution needs to be applied in interpreting the final shear wave model.
Direct Measurement
The velocity of a geological outcrop is directly measured at ultrasonic or sonic frequencies.
How can we help?
Fill in the contact form below. We respond to all weekday enquiries within 24 hours





